Misją Instytutu jest dzialalność naukowo-badawcza prowadząca do nowych rozwiązań technicznych i organizacyjnych użytecznych w kształtowaniu warunków pracy zgodnych z zasadami bezpieczeństwa pracy i ergonomii oraz ustalanie podstaw naukowych do właściwego ukierunkowywania polityki społeczno-ekonomicznej państwa w tym zakresie.
PRINCIPLES OF ASSESSMENT OF EXPOSURE TO INFRASONIC NOISE
BASIC CONCEPTS RELATED TO INFRASONIC NOISE IN THE WORK ENVIRONMENT
The basic issues and concepts related to infrasonic noise, such as sound, frequency and sound pressure, are the same as those related to noise in the audible range. The main differences between noise and infrasonic noise concern the frequency range of vibrations of an elastic medium (acoustic waves) that create a given type of noise and the quantities used to characterise a given type of noise in the work environment. This description only covers the topics and concepts that are mainly related to infrasonic noise. The basic concepts relating to both types of noise are discussed in the noise section.
Infrasonic noise
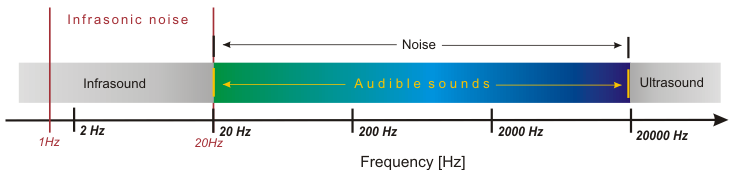
Infrasonic noise is defined as noise comprising sounds with frequencies from 1 Hz to 20 Hz. The range of infrasonic noise on the noise frequency scale is shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Infrasonic noise on the frequency axis.
Quantities used for the assessment of infrasonic noise
Infrasonic noise at workplaces is characterised by:
-
equivalent G-weighted sound pressure level, normalised to the 8-hour daily or the average weekly working time specified in the Labour Code (exceptionally in the case of the impact of infrasonic noise on the human body unevenly on individual days of the week),
-
equivalent G-weighted sound pressure level during the employee's stay at the workplace.
INFRASONIC NOISE LIMIT VALUES
Table 1 shows the values of infrasonic noise specified in the PN-Z-01338:2010 standard due to the nuisance criterion.
Table 1. The values of infrasonic noise specified in the PN-Z-1338:2010 standard due to the annoyance criterion
| Quantity | Value |
| Equivalent G-weighted sound pressure level, normalised to the 8-hour daily or the average weekly working time specified in the Labour Code (exceptionally in the case of the impact of infrasonic noise on the human body unevenly on individual days of the week). | 102 dB |
| Equivalent G-weighted sound pressure level during the employee's stay at the workplace | 86 dB |
Table 2 shows the limit values for infrasonic noise for adolescent workers and pregnant women (the same limit value was set for both of these groups of workers).
Table 2. Limit values of infrasonic noise for adolescent workers and pregnant women.
Table 2. Limit values of infrasonic noise for adolescent workers and pregnant women.
| Quantity characterizing infrasonic noise | Limit value |
| Equivalent G-weighted sound pressure level, normalised to the 8-hour daily or the average weekly working time specified in the Labour Code (exceptionally in the case of the impact of infrasonic noise on the human body unevenly on individual days of the week). | 86 dB |